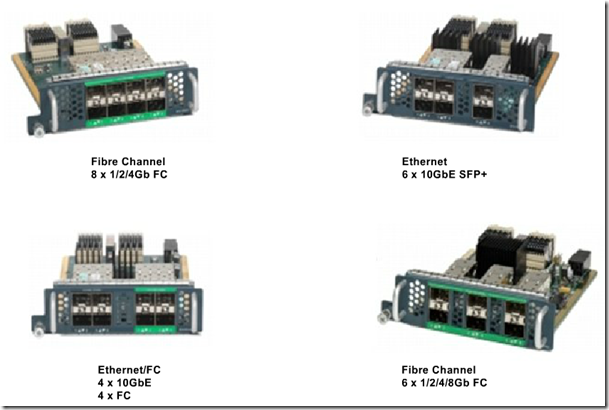
Data Center Components
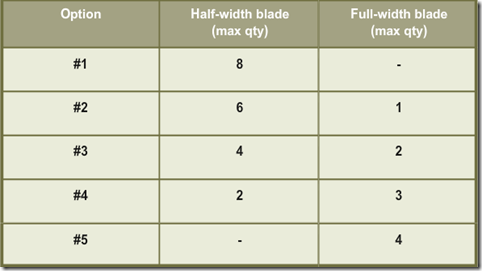
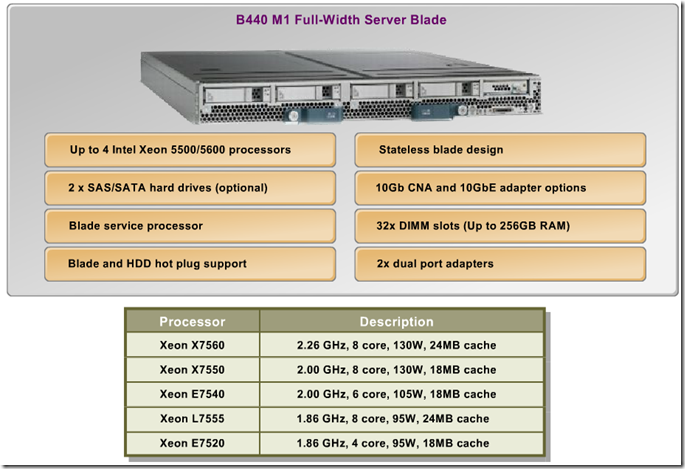
B230 M1
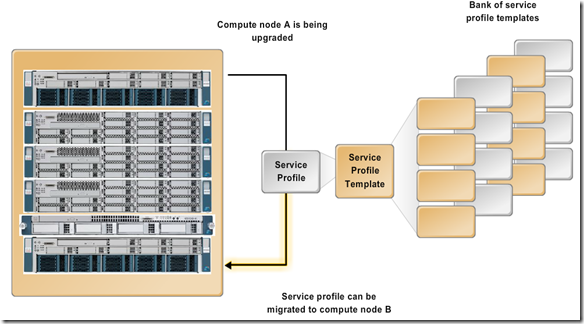
* Stateless Computing – Server Profile – MAC, WWN, IP, Firmware, BIOS, VLAN, ACL etc
Service Profile – Personality – MACS, WWN, UUIDs
Service Profile – Server Resources – vNIC and VHBAs
Service Profile – Behavior – Qos, Firmware etc – abstract hardware
Nexus 2K – Fabric Extender to support 1G Connection for FCOE
Nexus 2K & 5K acts single virtual Switch
CNA – Convergency Network Adpater ?
Nessus7K – HA, Support VDC up to 4 par
UCS VIC M81KR with FI ?
Remove software virtual switch, Replace software based switching on esx with asic based on FI, VN-Link, VIC can be both hw or virtual but CNA only work with Nessus 1000v
UCS P81E Virtual Interface with UCS Server
Support up to 128 PCIe vNIC, dynamic provisioning of vNIC and vHBA, VN-Link
Standard Mode: 1-1 VMC –> PCIe by VIC. All traffic sent to upstream FI for switching
High Performance Mode: by passing VM IO. Direct connect VIC, eliminate a complete memory copy in hypervisor. Performance Gain 50% more
VN-LINK – Move Data Link to VM layer
Issues addressed by Cisco UCS
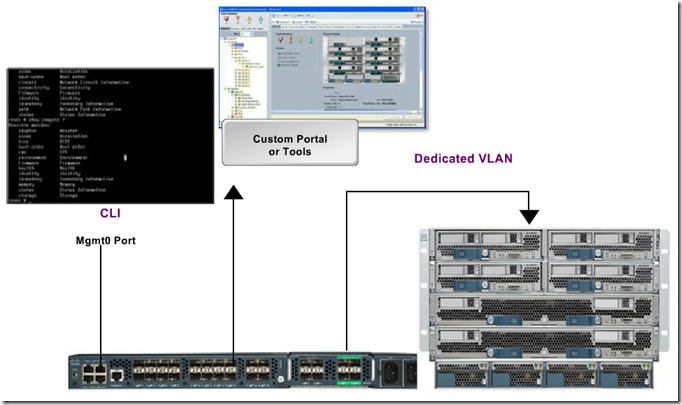
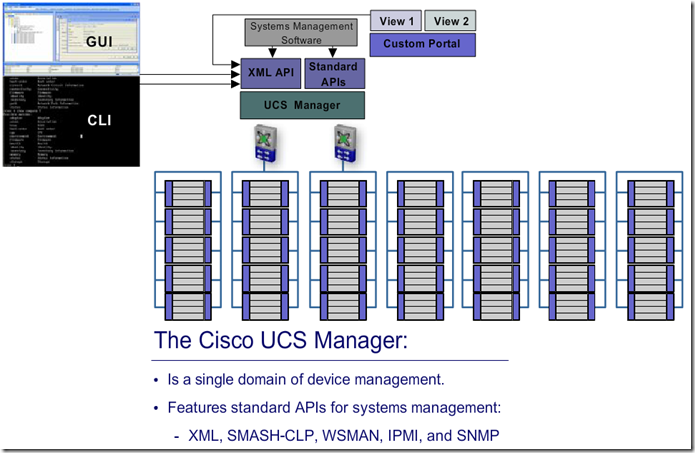
UCS Management
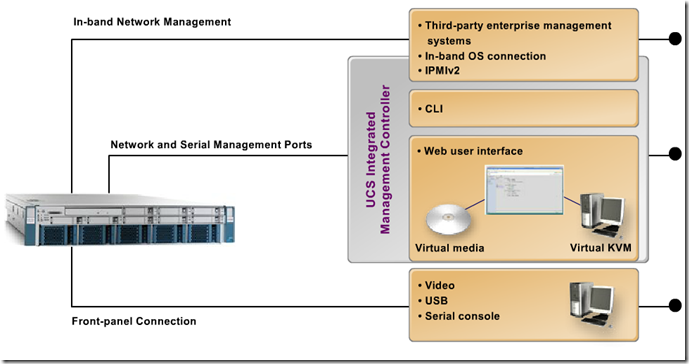
Front Panel : Video USB Serial
Ethernet Connects Cisco Integrated Controller CIMC runs on Baseboard Management Controller BMC
Inband -
Outband – IPMI2, CLI, Web interface
LOM : Lan on Motherboard
N+1 vs Grid Redundancy : twice the non-redundancy-survive the loss of an entire power grid within dc
Inbound and Outbound: inbound not redudant, Outbound redudant N+1
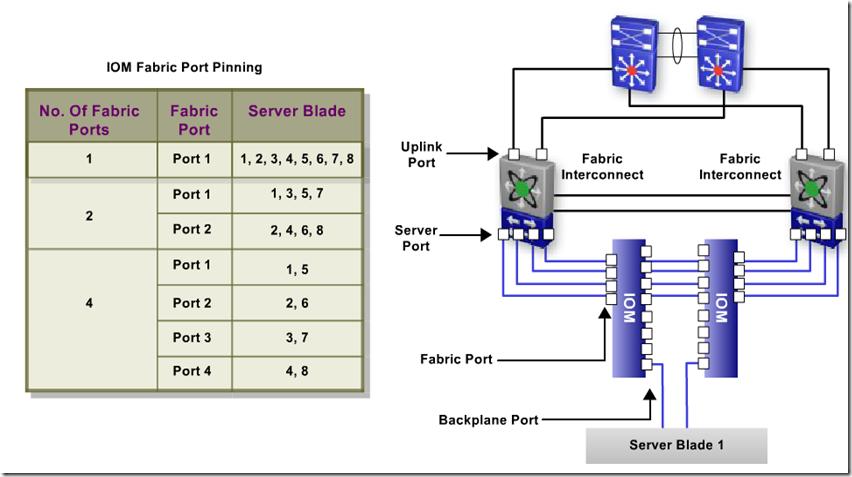
UCS Fabric Interconnect / Fabric Switches
not for non-UCS hardware, cannot upgrade to Nexus 5000
Fabric Extender
IO MUX – flexible bandwidth alloc between blade and fabric switch, transparent to user, managed by CAM.
Chase Management Controller CMC – service processor, HA with another fabric extender/CMC, discover hw
Storage Management
Top of Rack, End of Row or Middle of Row
Summary of Top of Rack advantages (Pro’s):
- Copper stays “In Rack”. No large copper cabling infrastructure required.
- Lower cabling costs. Less infrastructure dedicated to cabling and patching. Cleaner cable management.
- Modular and flexible “per rack” architecture. Easy “per rack” upgrades/changes.
- Future proofed fiber infrastructure, sustaining transitions to 40G and 100G.
- Short copper cabling to servers allows for low power, low cost 1oGE (10GBASE-CX1), 40G in the future.
- Ready for Unified Fabric today.
Summary of Top of Rack disadvantages (Con’s):
- More switches to manage. More ports required in the aggregation.
- Potential scalability concerns (STP Logical ports, aggregation switch density).
- More Layer 2 server-to-server traffic in the aggregation.
- Racks connected at Layer 2. More STP instances to manage.
- Unique control plane per 48-ports (per switch), higher skill set needed for switch replacement.
10GE CNA
CISCO UCS Power Calculator & TCO Advisor
URL: http://www.myciscocommunity.com
Position of Rack: http://bradhedlund.com/2009/04/05/top-of-rack-vs-end-of-row-data-center-designs/
Q/A
Support Boot from SAN ?
![image_thumb1_thumb[3] image_thumb1_thumb[3]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEithyphenhyphenohNnYUUPIzY_6GBnfDU2gXGGw_j0Bu18dkAUlE2M9CtHhMqU4X3BRicseFuwrtwXwX8aZ-3MvT83n7aZMCQWliUJDjl7TO8-u2XQOWppSwVBbYRCa7fyt-7ltsOumWcDByPXAoXUc/?imgmax=800)
![image_thumb5_thumb[1] image_thumb5_thumb[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhRPrJHwax3QyrvqGUhU3mnxBKerv6qtIrq7kV4s1UnkwH7l_qj68d_5lfpXfFM9N8sCYmWBDLHVVIggjpQ7nsRgKO3365hRP_vwvsHKUETizSKFzd3L2P__EkOijJJ6uGQ1bok_NRYiHA/?imgmax=800)


![image_thumb11_thumb[1] image_thumb11_thumb[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh-lcgVec9PruS89j_CCWLHBLiaaXXSooSuSbojQypv36_DzkGo2pU2RTqEQlOhmW54kE-NEdl1A61ioDSUNDziphW20N84yRJki05bvYkEBDbFJvHHDLYZB3eQw0UvBHfzqORFlhGzvAU/?imgmax=800)
![image_thumb14_thumb[1] image_thumb14_thumb[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEigPsQjM9VKOVqMr94USq3q3-Ou0lpugkGczckh-W1krf5jxJK9Ng6vj1L8z6Yx1BSokYUlLv2xW1KVaBI8N7E5TbJ6OTl8jgO-kgd-Rn4uDdCGAf8Qa-hZV-qz8z4XmqcM8cIyQRtF_qM/?imgmax=800)
![image_thumb1_thumb[5] image_thumb1_thumb[5]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEh8r5c6Z7nOAunqcUmih4cqPI9hVtAqJshBU98fQCdGEPWxV1uJWzJ43QrP-8PJ-tzOJ6NeNI3i6RZHHQWFCHFOCjAYsN4mBgDMLKj1c0747lDSxx9bjPQ0wqoUTofbfXuGy5yNH0T18J4/?imgmax=800)
![image_thumb4_thumb[1] image_thumb4_thumb[1]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhhcIq-6sZ4x58fTkEYvMeNFtuRJb8t4W4VtFvhvAznyHfGN3WFKJ3AY8JOTNA9Snl7hZKaTIiZYandPQO9KFFUGCHdv5MTnzeyM7-C5V_os1NdQ-DAo0HB0EI-1GYtO5Svj-7PrgAd32A/?imgmax=800)
![image_thumb1_thumb[4] image_thumb1_thumb[4]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEhtweaX_iOgae8RguOcMShhhMNNmGve-0xuQcKy0SlPAqKkYQpGHFNPaQ3zXFqudi9nBM4cBsAMDAvDOcfUaKSSDPd2HpvTTK99Erl84JPfFGqfq2_DAtxvL8ofprRifB_EWzOkYp3KEH0/?imgmax=800)
![image_thumb5_thumb[2] image_thumb5_thumb[2]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEiddKGMTtxUQ1Hr5cI3KczCBNtd1mBUX5vGXBiJxu90xrzyAaEcWqTr3hAACYNPIpzc8JbjiklY1jEkfQ5FPj5HfeIhqnzT68M_6VLhu2S_vkm9qSSXRtZto2cZ8qZFmxw20JtbUVk051k/?imgmax=800)

![image_thumb11_thumb[2] image_thumb11_thumb[2]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEjpl3TilBBK3WpzDgVx8x6Omic3obdCGKbjBiKUY3GqpGFzM3gkoFYyO8VfxliBuAROAOFj5BSuzgwtLJcRTs3emC5SrcCnsL-eK7vxHXdJwfFZcaFghSWpgRIV7PQtlTV14hzshU6U4VE/?imgmax=800)
![image_thumb14_thumb[2] image_thumb14_thumb[2]](https://blogger.googleusercontent.com/img/b/R29vZ2xl/AVvXsEi0_nRgB1lP4AulUI_R2Rz2KS3L7wtM6aWzA4Gv-cN7Sk7KOfMgbya1uPZPe5lNVjlulNpRD6NIzNTbukklJ52kbq-YHs9Acv1qTcYQgOkf_n9fptRIhG-GJx6gdFIq3O3hPPDLx-saC8Q/?imgmax=800)